EBA cooperation with EU institutions and international partners
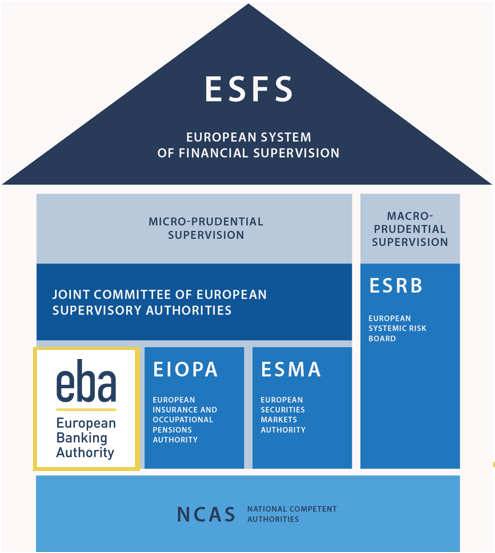
The EBA is part of the European System of Financial Supervision (ESFS), which was established in 2010 following the 2008-09 financial crisis and builds on the de Larosière report.
The ESFS sets out multi-layered system of micro- and macro-prudential authorities. It includes the European Systemic Risk Board (ESRB), the three European supervisory authorities (ESAs), namely the EBA, the European Insurance and Occupational Pensions Authority (EIOPA), the European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA), and competent authorities.
The EBA cooperates closely with a wide range of EU institutions and authorities such as the European Commission, the European Parliament and the Council. This also includes the European Central Bank (ECB) and the Single Resolution Board (SRB) to ensure effective supervision and financial stability.
Within the ESFS, the EBA works with EIOPA and ESMA, including through the ESAs Joint Committee. Together they monitor cross-sectoral risks and tackle issues related to digital operational resilience, consumer protection, securitisation, financial conglomerates, and sustainable finance, amongst others. The EBA also participates in discussions in the ESRB, including in its General Board and Steering Committee. The two institutions cooperate at technical level on macroprudential and systemic risk issues, including in the development of the EBA’s EU-wide banking stress test.
The EBA also relies on strong cooperation with competent authorities from the EU and EEA-EFTA member states in the development of policy products and other mandates. The heads of banking supervision in those national authorities sit in the EBA’s main decision-making body, the Board of Supervisors.
International cooperation
The EBA engages internationally with key financial institutions to promote the development and adoption of sound regulatory and supervisory prudential standards worldwide. This includes active participation in international standard setter bodies such as the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision (BCBS), the Financial Stability Board (FSB), as well as collaboration with key international institutions like the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD).
The EBA also fosters regulatory and supervisory cooperation with non-EU jurisdictions and their relevant authorities. It does so through its contribution to equivalence assessments of prudential frameworks, confidentiality regimes, the negotiation of bilateral or multilateral agreements, and participation in international regulatory dialogues.
